Anatomy
Physical Therapy in Pittsburgh for Ankle Impingement
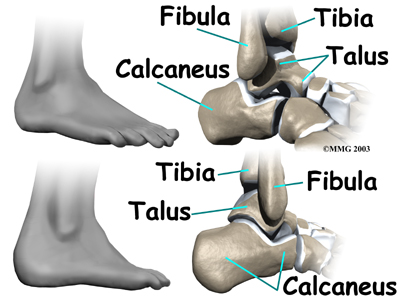
Welcome to Greater Pittsburgh Physical Therapy & Sports Medicine's overview of the anatomy of the ankle.
The ankle joint is formed where the bones of the lower leg, the tibia and the fibula, connect above the anklebone, called the talus. The tibia is the main bone of the lower leg. The fibula is the small, thin bone along the outer edge of the tibia.
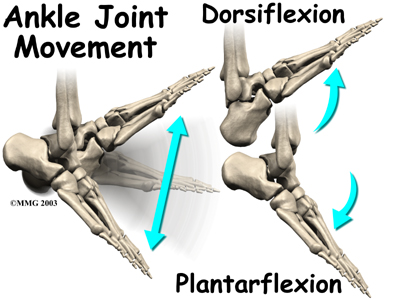
The ankle joint is a hinge that allows the foot to move up (dorsiflexion) and down (plantarflexion). The ankle is a synovial joint, meaning it is enclosed in a joint capsule that contains a lubricant called synovial fluid.
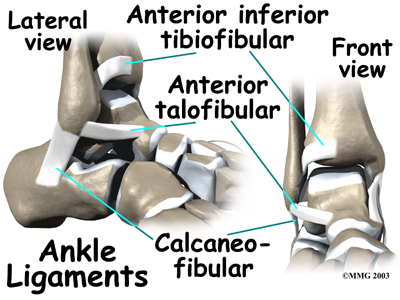 Strong ligaments surround and support the ankle joint. The ligament that crosses just above the front of the ankle and connects the tibia to the fibula is called the anterior inferior tibiofibular ligament (AITFL). The anterior talofibular ligament (ATFL) supports the outer edge of the ankle. The ATFL goes from the tip of the fibula and angles forward to connect with the talus.
Strong ligaments surround and support the ankle joint. The ligament that crosses just above the front of the ankle and connects the tibia to the fibula is called the anterior inferior tibiofibular ligament (AITFL). The anterior talofibular ligament (ATFL) supports the outer edge of the ankle. The ATFL goes from the tip of the fibula and angles forward to connect with the talus.
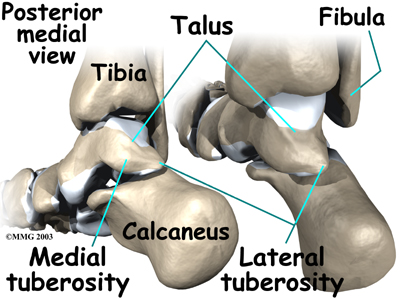
The talus rests on the the heelbone (the calcaneus). The joint formed between these two bones is called the subtalar joint. The calcaneus extends backward below the ankle, forming a shelf on which the talus rests.
Two small bony bumps, called tuberosities, project from the back of the talus, one on the inside (medial) edge and one on the outer (lateral) edge.
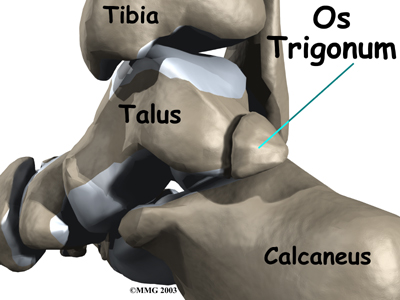
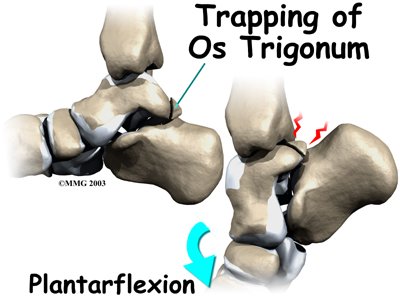
In some people the lateral tuberosity is not united to the talus. The separate piece of bone is called an os trigonum. This separation of the os trigonum from the talus is usually not a fracture. About 15 percent of people have an os trigonum. An os trigonum sometimes causes problems of impingement in the back of the ankle.
Related Document: Greater Pittsburgh Physical Therapy & Sports Medicine's Guide to Ankle Anatomy
#testimonialslist|kind:all|display:slider|orderby:type|filter_utags_names:Foot therapy|limit:15|heading:Hear from some of our *Foot Therapy* patients#
Causes
Pinching of tissues in the front of the ankle is called anterior impingement. Athletes who have had several mild ankle sprains or one severe sprain are most likely to have anterior impingement. This is especially true for athletes who repeatedly bend the ankle upward (dorsiflexion), such as baseball catchers, basketball and football players, and dancers. Over time, irritation along the front edge of the ankle can lead to impingement.
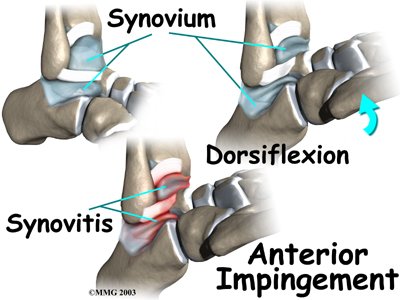 Irritation in the lower edge of the AITFL and the front of the ATFL can thicken these ligaments. The irritated ligaments become vulnerable to getting pinched between the tibia and talus as the foot is dorsiflexed. These ligaments may also begin to rub on the joint capsule of the ankle. This can inflame the synovial lining of the capsule, a condition called synovitis.
Irritation in the lower edge of the AITFL and the front of the ATFL can thicken these ligaments. The irritated ligaments become vulnerable to getting pinched between the tibia and talus as the foot is dorsiflexed. These ligaments may also begin to rub on the joint capsule of the ankle. This can inflame the synovial lining of the capsule, a condition called synovitis.
A similar problem can happen after an ankle sprain. As the torn or ruptured ligament heals, the body responds by forming too much scar tissue along the front and side of the ankle joint. This creates a small mass of tissue called a meniscoid lesion. Dorsiflexing the ankle can trap the tissue between the edge of the ankle joint, causing pain, popping, and a feeling that the ankle will give out and not support your body weight.
Over time, damage from past ankle sprains may also lead to the formation of small projections of bone called bone spurs. Bone spurs can form along the bottom ledge of the tibia bone or on the upper surface of the talus. As the ankle hinges into dorsiflexion, the bone spurs may begin to jab into the soft tissues along the front edge of the ankle joint, causing symptoms of anterior impingement.
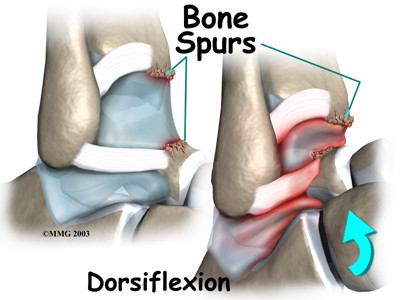
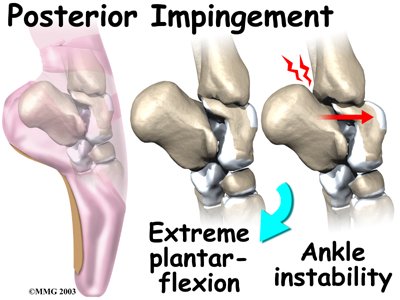
Posterior impingement occurs in the back of the ankle. It is most common in ballet dancers who must continually rise up on their toes, pointing their foot downward into extreme plantarflexion. Other athletes are rarely affected but may have problems if they routinely plantarflex their feet.
The usual cause of posterior impingement is an os trigonum (described earlier). This normal fragment of bone is a separation of the lateral tuberosity from the talus. When an os trigonum is present, it can cause problems, especially among ballet dancers who constantly rise up on their toes into the dance position called pointe. Pointe is a position of extreme ankle plantarflexion. As the foot points downward sharply, the os trigonum can get sandwiched between the bottom edge of the tibia and the top surface of the calcaneus (the heelbone). This can trap the tissues above and below the os trigonum, leading to symptoms of posterior impingement.
Posterior impingement can also occur in a ballet dancer who has had a previous ankle sprain. Damage from the past ankle sprain may create too much instability in the ankle. As the dancer rises up on the toes, the talus may be free to slide forward slightly. This allows the shelf of the heelbone to come into contact with the back of the tibia, pinching the soft tissues in between. Posterior impingement from ankle instability can also happen in other athletes. But this is uncommon, because forceful plantarflexion is rarely required in other sports.
Related Document: Greater Pittsburgh Physical Therapy & Sports Medicine's Guide to Ankle Sprain and Instability
Symptoms
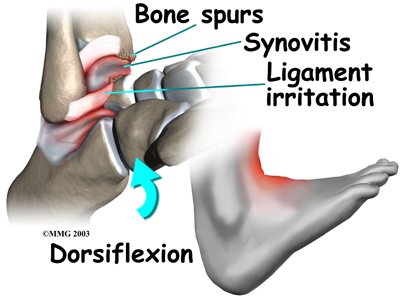 Anterior impingement may feel like ankle pain that continues long after an ankle sprain. The ankle may feel weak, like it can't be trusted to hold steady during routine activities. When anterior impingement comes from ligament irritation, pain and tissue thickening are usually felt in front and slightly to the side of the ankle. This is the area of the ATFL. The pain worsens as the foot is forced upward into dorsiflexion. If the ligaments have irritated the synovium of the ankle joint capsule, throbbing pain and swelling from inflammation (synovitis) may also be felt in this area.
Anterior impingement may feel like ankle pain that continues long after an ankle sprain. The ankle may feel weak, like it can't be trusted to hold steady during routine activities. When anterior impingement comes from ligament irritation, pain and tissue thickening are usually felt in front and slightly to the side of the ankle. This is the area of the ATFL. The pain worsens as the foot is forced upward into dorsiflexion. If the ligaments have irritated the synovium of the ankle joint capsule, throbbing pain and swelling from inflammation (synovitis) may also be felt in this area.
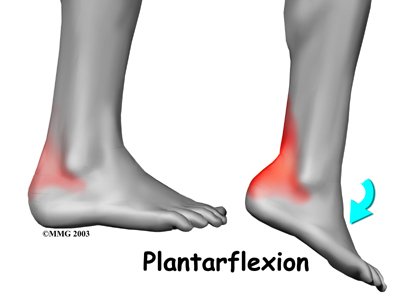
Symptoms of posterior impingement include pain behind the heel or deep in the back of the ankle. There is usually tenderness just behind the bottom tip of the fibula, by the outer ankle bone. Pain is usually worse when the foot is pointed down into plantarflexion. A painful clicking sensation may also be felt as the foot is twisted in and out.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of ankle impingement is usually made by examining the ankle. Our Physical Therapist will manipulate your ankle to see which movements or positions cause your pain. If anterior impingement is suspected, we may bend your ankle upward or ask you to squat down. To check for posterior impingement, our therapist may push your foot downward or have you rise up on your toes. Tenderness can usually be pinpointed over the tissues that are being pinched.
Your Physical Therapist at Greater Pittsburgh Physical Therapy & Sports Medicine may also refer you to a doctor for X-rays or other diagnostics helpful in accurately assessing your ankle impingement.
Our Treatment
Non-surgical Rehabilitation
Even if you don't require surgery, you may need to follow a program of rehabilitation exercises. The Physical Therapists at Greater Pittsburgh Physical Therapy & Sports Medicine can create a program to help you regain ankle function. It is very important that you improve strength and coordination in the ankle.
Initially our Physical Therapist will advise you to rest the ankle for a short time to reduce swelling and pain. A special walking boot or short-leg cast may be recommended to restrict ankle movement for up to four weeks. Patients may also want to consult with their doctor or pharmacist regarding mild pain medications and anti-inflammatory medicine, such as ibuprofen. An ice pack can also help alleviate swelling and may encourage a faster return of normal ankle movement.
Once you begin your Greater Pittsburgh Physical Therapy & Sports Medicine rehabilitation program, your recovery may involve doing a series of exercises including stationary cycling, range of motion, and ankle strengthening.
Post-surgical Rehabilitation
After debridement surgery, patients are usually placed in an ankle splint, and begin their recovery by using crutches. The amount of weight put on the foot is gradually increased over a period of approximately one to two weeks. Although recovery time varies among individuals, our patients generally advance quickly in rehabilitation and are often able to resume normal activity within four to six weeks.
Rehabilitation after excision of the os trigonum is a slower process. We may advise you to attend therapy sessions for two to three months, with full recovery sometimes taking up to six months. Patients are often kept in the ankle splint for up to two weeks, and crutches are used during this time as the amount of weight borne on the foot is gradually increased.
After removing the stitches and the ankle brace, our patients are often able to begin formal Physical Therapy. When you start your rehabilitation program at Greater Pittsburgh Physical Therapy & Sports Medicine, initial treatments begin with gentle range-of-motion exercises for the ankle and toes. The first few Physical Therapy treatments are also designed to help control pain and swelling from the surgery. Our therapist may use ice, electrical stimulation treatments, massage and other hands-on procedures to ease muscle spasm and pain.
As the symptoms from surgery begin to ease, our Physical Therapist may show you how to do easy ankle motions on a stationary bicycle. After three or four weeks we may advise you to start doing more active ankle exercises. Exercises are used to improve the strength in the ankle muscles. Our therapist will also help you regain position sense in the ankle joint to improve its stability.
At Greater Pittsburgh Physical Therapy & Sports Medicine, our goal is to help you keep your pain under control, improve your range of motion, and maximize strength and control in your ankle. When your recovery is well under way, regular visits to our office will end. We will continue to be a resource, but you will be in charge of doing your exercises as part of an ongoing home program.
Greater Pittsburgh Physical Therapy & Sports Medicine provides Physical Therapy services in Pittsburgh.
Physician Review
Your doctor will probably order X-rays if impingement is suspected. X-rays can show if there are bone spurs on the tibia or talus. In cases of posterior impingement, an X-ray can show if an os trigonum is present. You may be asked to squat down or rise up on your toes during the X-ray. This helps show if impingement is due to bone pinching the soft tissues.
A bone scan may be recommended in select cases, such as when surgery is being considered. In general, MRI scans are not helpful for impingement problems, but they may be ordered to check for other ankle problems that could be causing your pain.
If the doctor believes that pinching in the back of the ankle is from an os trigonum, a numbing medication may be injected into this area. If it feels better, the problem is a posterior impingement from the os triogonum. If the pain doesn't change, the problem could be in the tendon that runs along the inside edge of the os trigonum.
Your doctor may recommend a steroid injection into the painful area. Steroids are strong anti-inflammatory medications. A steroid injection can help relieve irritation and swelling in the soft tissues that are being pinched, reducing their tendency to get pinched.
Surgery
If nonsurgical treatments do not work, surgery may be recommended. The type of surgery will vary depending on the location and cause of ankle impingement.
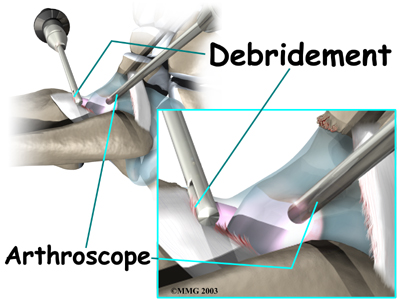
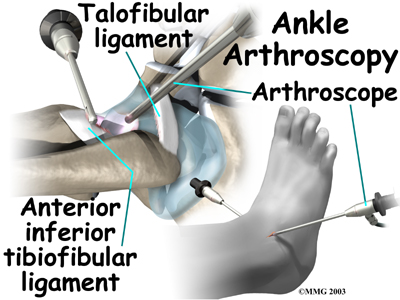 Debridement is the most common surgery for anterior ankle impingement. Many surgeons prefer to perform this procedure with an arthroscope. An arthroscope is a tiny TV camera that can be inserted into a very small incision. It allows the surgeon to see the area where he or she is working on a TV screen.
Debridement is the most common surgery for anterior ankle impingement. Many surgeons prefer to perform this procedure with an arthroscope. An arthroscope is a tiny TV camera that can be inserted into a very small incision. It allows the surgeon to see the area where he or she is working on a TV screen.
To begin, two small incisions are made through the skin on each side of the impingement area. The surgeon inserts the arthroscope to see which area of the tendons or joint capsule are irritated and thickened. The arthroscope lets the doctor see if a meniscoid lesion (mentioned earlier) is present. A small shaver is used to clear away (debride) irritated tissue from the affected ligaments. The surgeon also debrides the tissue forming a meniscoid lesion and any areas of the joint capsule that are inflamed. Small forceps may also be used to clear away irritated or inflamed tissue.
Debridement
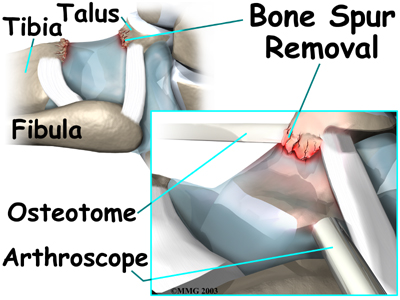
Small bone spurs on the tibia or talus are removed. If the spurs are large, the surgeon may decide to create a new incision over or next to the spur. This allows a special instrument, called an osteotome, to be inserted. The surgeon uses the osteotome to carefully remove these larger bone spurs.
Bone Spur Removal
Before concluding the procedure, a fluoroscope is used to check the debridement and to make sure no bony fragments remain. A fluoroscope is a special X-ray machine that allows the surgeon to see a live X-ray picture on a TV screen during surgery. When the surgeon is satisfied that debridement and removal of bone fragments is complete, the skin is stitched together.
Os Trigonum Excision
The goal of an os trigonum excision is to carefully remove (excise) the os trigonum to alleviate pinching of the tissues above or below it. It is standard to use an open surgical method which requires a one- to two-inch incision over the outer part of the back of the ankle. An arthroscope is not routinely used for os trigonum excision because there are many nerves and blood vessels in the back of the ankle that could be injured by an arthroscope.
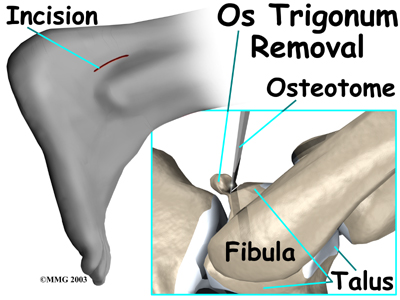 This surgery begins by placing the patient face down on the operating table. The surgeon makes a small incision over the lateral side of the back of the ankle, just behind the outer anklebone. A retractor is used to carefully hold the nearby tendons, nerves, and blood vessels out of the way. The surgeon locates the os trigonum. A scalpel is usually sufficient to dissect the os trigonum. However, if a bony bridge binds the os trigonum to the talus, the surgeon may need to use a chisel or osteotome.
This surgery begins by placing the patient face down on the operating table. The surgeon makes a small incision over the lateral side of the back of the ankle, just behind the outer anklebone. A retractor is used to carefully hold the nearby tendons, nerves, and blood vessels out of the way. The surgeon locates the os trigonum. A scalpel is usually sufficient to dissect the os trigonum. However, if a bony bridge binds the os trigonum to the talus, the surgeon may need to use a chisel or osteotome.
A fluoroscope is used to check for any remaining bony fragments. When the surgeon is satisfied that all bone fragments have been removed, the skin is stitched together. Patients are placed in a special splint designed to protect the ankle and to keep the foot from pointing downward.
Portions of this document copyright MMG, LLC.
